INVENTORY CONTROL: The Standard Cost Inventory Valuation System Series
Standard Cost
Think of this as a benchmark or a budget. It’s the cost you expect to pay for making a product. This includes materials, labor, and overhead costs.
Actual Cost
This is the real cost you incur when you actually make the product.

Material Price Variance
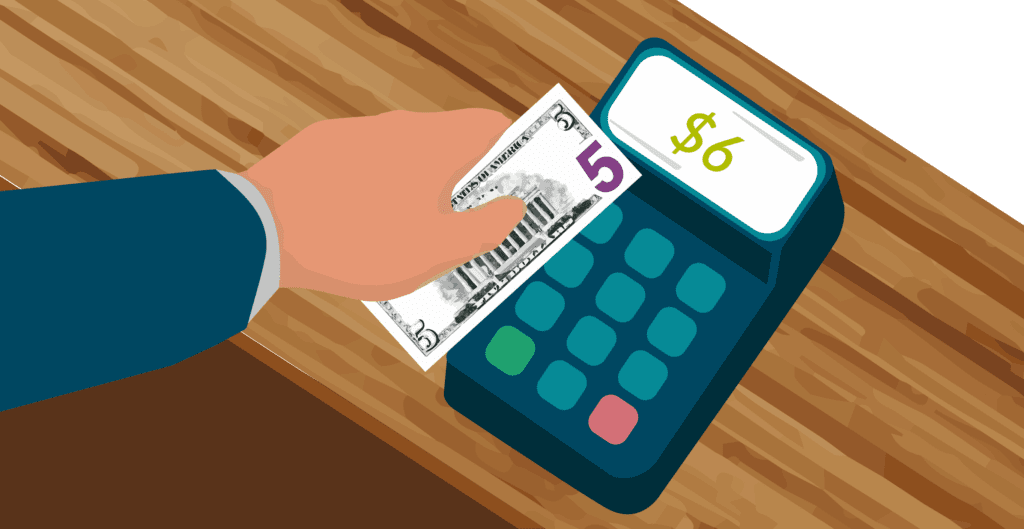
Definition
This happens when the price you paid for the materials is different from what you expected.
Example
If you expected to pay $5 per unit of material but ended up paying $6, the price variance is $1 per unit.
Material Quantity Variance

Definition
This occurs when the amount of materials used is different from what you expected.
Example
If you expected to use 10 units of material to make a product but actually used 12 units, the quantity variance is 2 units.
Labor Price Variance

Definition
This happens when the wage rate you paid for labor is different from what you expected.
Example
If you expected to pay $5 per hour but ended up paying $6 hour, the price variance is $1 per hour.
Labor Quantity Variance

Definition
This occurs when the amount of time spent is different from what you expected.
Example
If you expected to spend 10 hours of time to make a product but actually spent 12 hours, the quantity variance is 2 hours.

Variable Spending Overhead Variance

Definition
The difference between what you expected to spend on variable overheads and what you actually spent.
Example
If you expected to spend $2,000 on electricity but actually spent $2,500, the spending variance is $500.
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance
Definition
The difference between the expected and actual usage of the activity base (like machine hours) that drives variable overhead costs.
Example
If you expected to use 100 machine hours but actually used 120 machine hours, the efficiency variance would be based on the cost per machine hours.

Fixed Overhead Budget (Spending) Variance

Definition
The difference between the actual fixed overhead costs and the budgeted fixed overhead costs.
Example
If you budgeted $5,000 for rent but actually spent $5,200, the spending variance is $200.

Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance
Definition
The difference between the budgeted fixed overhead costs based on standard production levels and the applied (or actual) fixed overhead costs based on actual production levels.
Example
If you budgeted fixed overhead for 1,000 units but actually produced 1,200 units, the volume variance would measure the effect of producing more or fewer units than expected.
Part II
Estimating Standard Costs
What To Consider
Part VI
Standard Cost Variances in a Work Order Environment





